Athena Review Image Archive ™
Chlamydomonas (green algae) cell
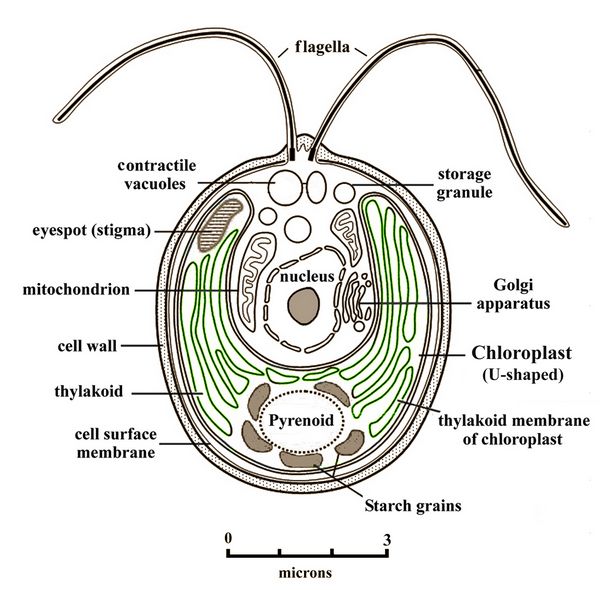
Cell of the green algae Chlamydomonas (after Falciatore et al. 2005.)
Chlamydomonas
is a genus of present-day green algae (Chlorophyta) found in
stagnant water, damp soil, fresh water, seawater, and snow. It belongs
to the Kingdom Viridiplantae, the division Chlorophyta, the
class Chlorophyceae, the order Volvocales, and the family
Chlamydomonodaceae.
Chlamydomonas has the form of unicellular flagellates which reproduce both sexually and asexually. A typical cell (illustrated here) is 5-7 microns in diameter, not including flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast genetics.
In addition to the normal rows of thylakoid membranes containing chlorophyll pigments for absorbing sunlight in photosynthesis, Chlamydomonas also possesses red eye spots which are sensitive to light and which determine movement. It contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) which are directly activated by light.
References:
A Falciatore, L Merendino, F Barneche, M Ceol, R Meskauskiene, K Apel, JD Rochaix. 2005. Genes & Development 19:176-187
.Copyright © 1996-2020 Rust Family Foundation (All Rights Reserved).