Athena Review Image Archive ™
Lampreys (Petromyzoniformes)
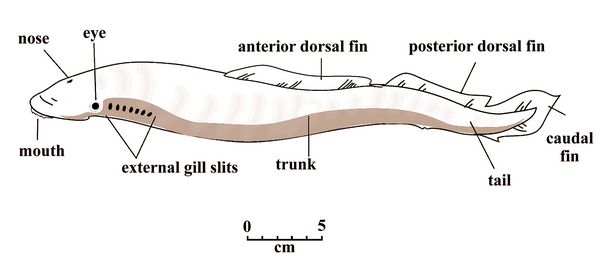
Lampreys (Petromyzoniformes) (after Forey and Janvier 1993).
Lampreys are a group of jawless fishes usually considered the most basal group of the Vertebrata. While they are a present day marine animal, their earliest known fossil taxa date from the Late Ordovician period, ca. 450 mya.
Since the time of Linnaeus (1758), lampreys and hagfish have been grouped in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata. Nearly fifty species of lampreys are known. They also belong to the superclass Agnatha, the class Hyperartia, and the order Petromyzontiformes, from Latin petra- "stone," and Greek -myzo- "to suckle," and Latin -forma "shape."
The lamprey uses its suction cup-like mouth to attach itself to the skin of a fish and rasps away tissue with its sharp, probing tongue and keratinized teeth. Secretions in the lamprey's mouth prevent the victim's blood from clotting. Some species live in fresh water for their entire lives. Others, like the sea lamprey, are anadromous. Their body length is 10- 90 cm. Lacking paired fins, adult lampreys have large eyes, one nostril on the top of the head, and seven gill pores on each side of the head.
The unique morphological characteristics of lampreys, such as their cartilaginous skeleton, suggest they are the sister taxon of all living jawed vertebrates (gnathostomes), and are usually considered the most basal group of the Vertebrates.
Recent molecular and morphological studies put lampreys and hagfish in the superclass Agnatha ("without jaws"). The other vertebrate superclass is Gnathostomata ("jawed mouths") including classes Chondrichthyes (sharks) and Osteichthyes (bony fish).
References:
Forey, P. and P. Janvier, 1993. Agnathans and the origin of jawed vertebrates. Nature 361:129-134.
Renaud, C.B., 2011. Lampreys of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of lamprey species known to date. FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. No. 5. Rome, FAO.
.Copyright © 1996-2020 Rust Family Foundation (All Rights Reserved).