Athena Review Image Archive ™
Roman road strata
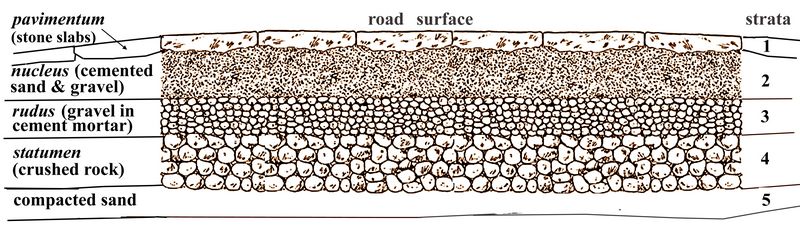
Cross section of strata or construction layers in Roman road building
The term strata,
derived from the ancient Romans, actually has two meanings; first,
layers or levels, and secondly, roads. Between 50 BC - AD 400,
the Romans built roads all over the Empire, from Spain to the Euphrates River,
whose straight courses are still followed today and built over by many
modern roads. The Roman roads were constructed in successive layers of
sand, loose stones, cemented gravel, concrete, and paving stones, as
shown in the figure. These gravel and pavement layers were called
strata, with a single layer called a stratum (from the Latin verb
sternere “to spread, scatter, or strew around” ).
In the case of
roads, the word stratum (the past participle of sternere) thus meant a
"spread layer" of gravel or paving stones. Paved Roman streets,
roads, and other thoroughfares were called strata via; with via, the
Latin preposition for “through,” used for paths, streets, and
roads not initially paved. Today one of the Italian words for street is
via, with strada used for road, and autostrada for highway. Also
derived from Roman strata via are the German word strasse for street,
and the Dutch word straat, closely linked with the Old English
straet (used, for example, in the 10th century Anglo-Saxon poem
Beowulf), and modern English street.
English and other modern
languages have also incorporated the ancient Latin terms strata and
stratum into generic terms to refer to any kind of layer or levels (as
in “stratified society,” “upper stratum,” “stratisphere,” and similar
phrases). The term strata was in this way used by 17th-19th century
European engineers and surveyers to describe specific layers of rock
encountered while digging mines, tunnels, or canals. Since then the
study of geological layering (including the layering of fossils) has
been known as stratigraphy, meaning "the mapping of layers."
Copyright © 1996-2020 Rust Family Foundation (All Rights Reserved).